3.2 Glaucoma Differential Diagnosis and Aetiologies
Contents
A. Primary
- Congenital (90% sporadic)
- Infantile
- Juvenile
B. Secondary
Anterior Segment Dysgenesis
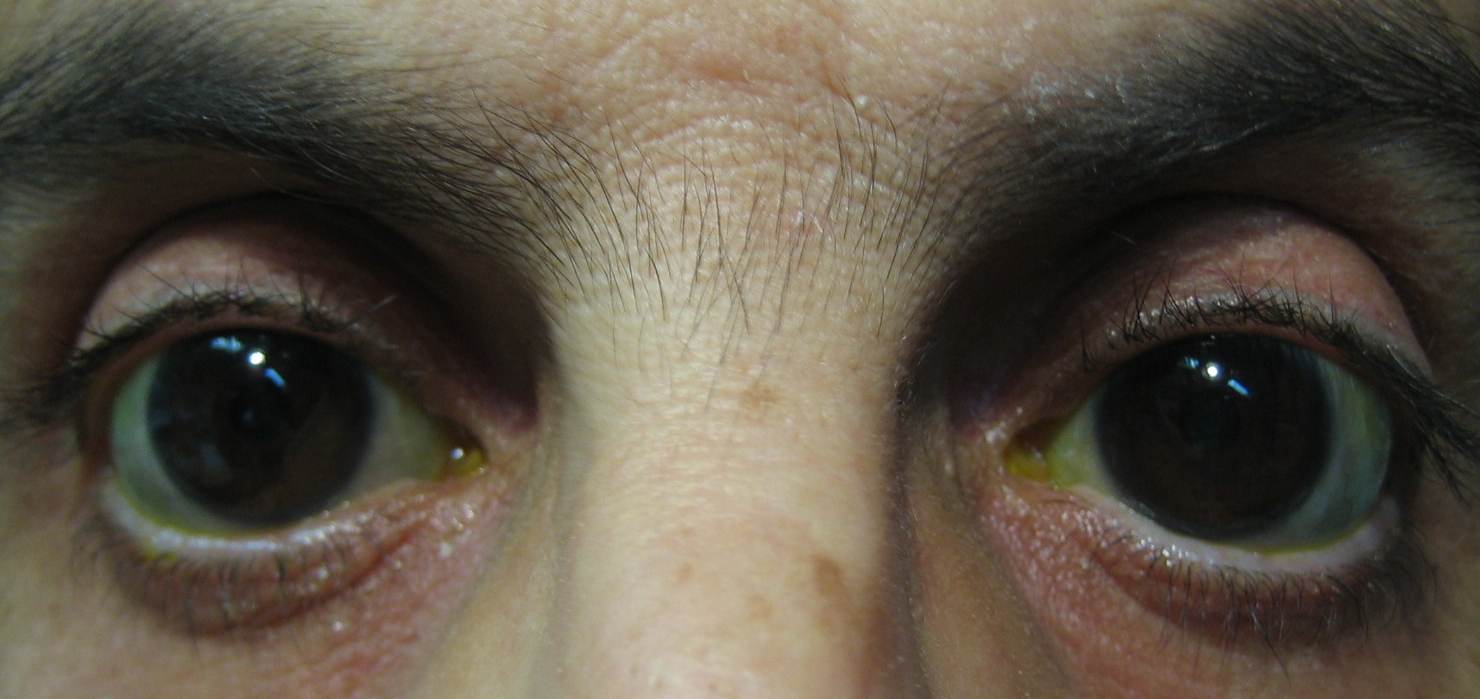
Aniridia, Peters, Axenfeld-Rieger
Uveitic
Rubella, JIA
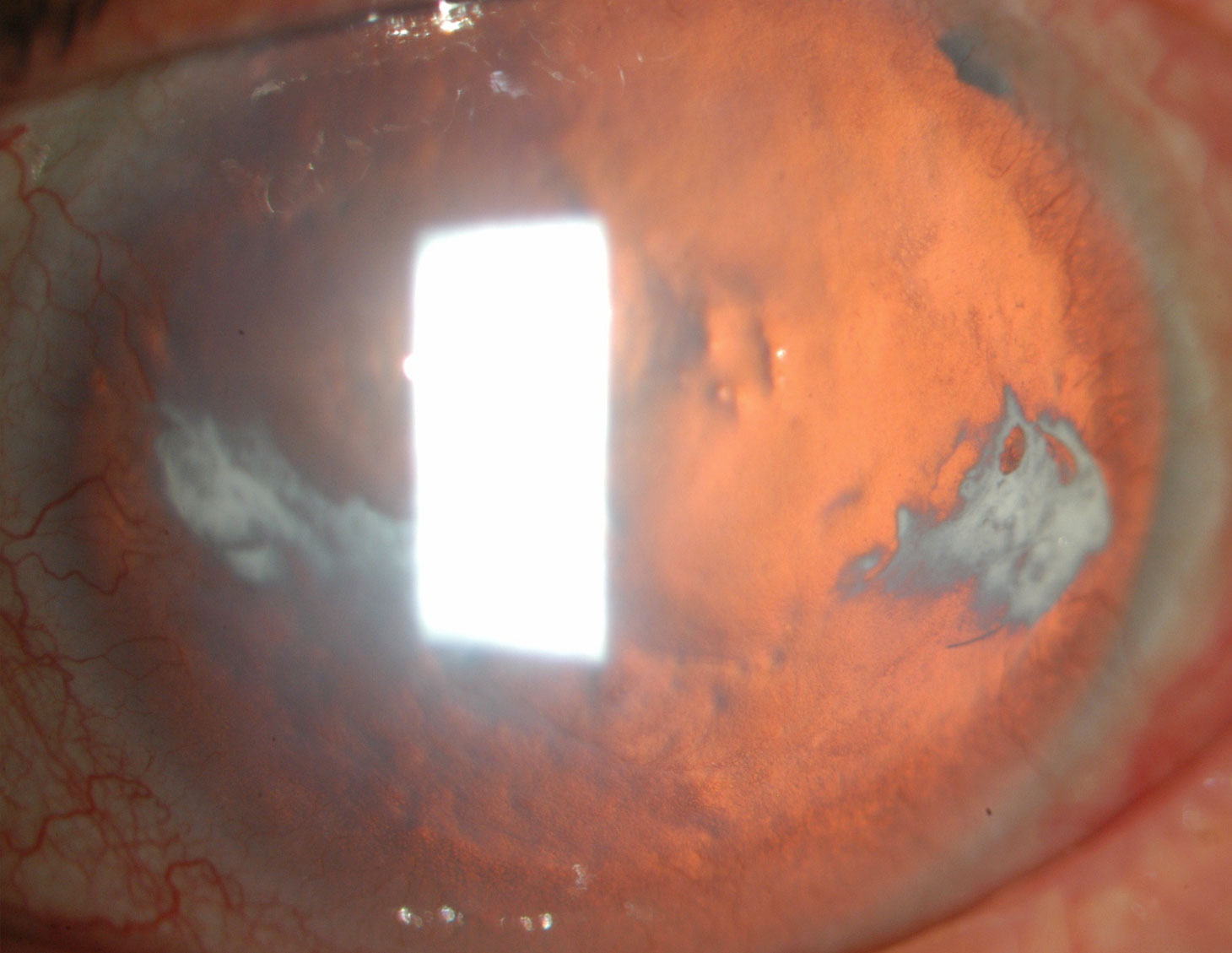
Lens
Aphakia
Retinal Vascular
PHPV
Systemic
Phakomatoses: Neurofibromatoses, Sturge Weber, Down, Marfans, Lowe syndrome
Trauma
Steroids
Patient Related
- Conjunctival scarring or inadequate conjunctiva
- Previous failed trabeculectomy
- Paediatric
Eye Related
- NVG
- Aphakic glaucoma
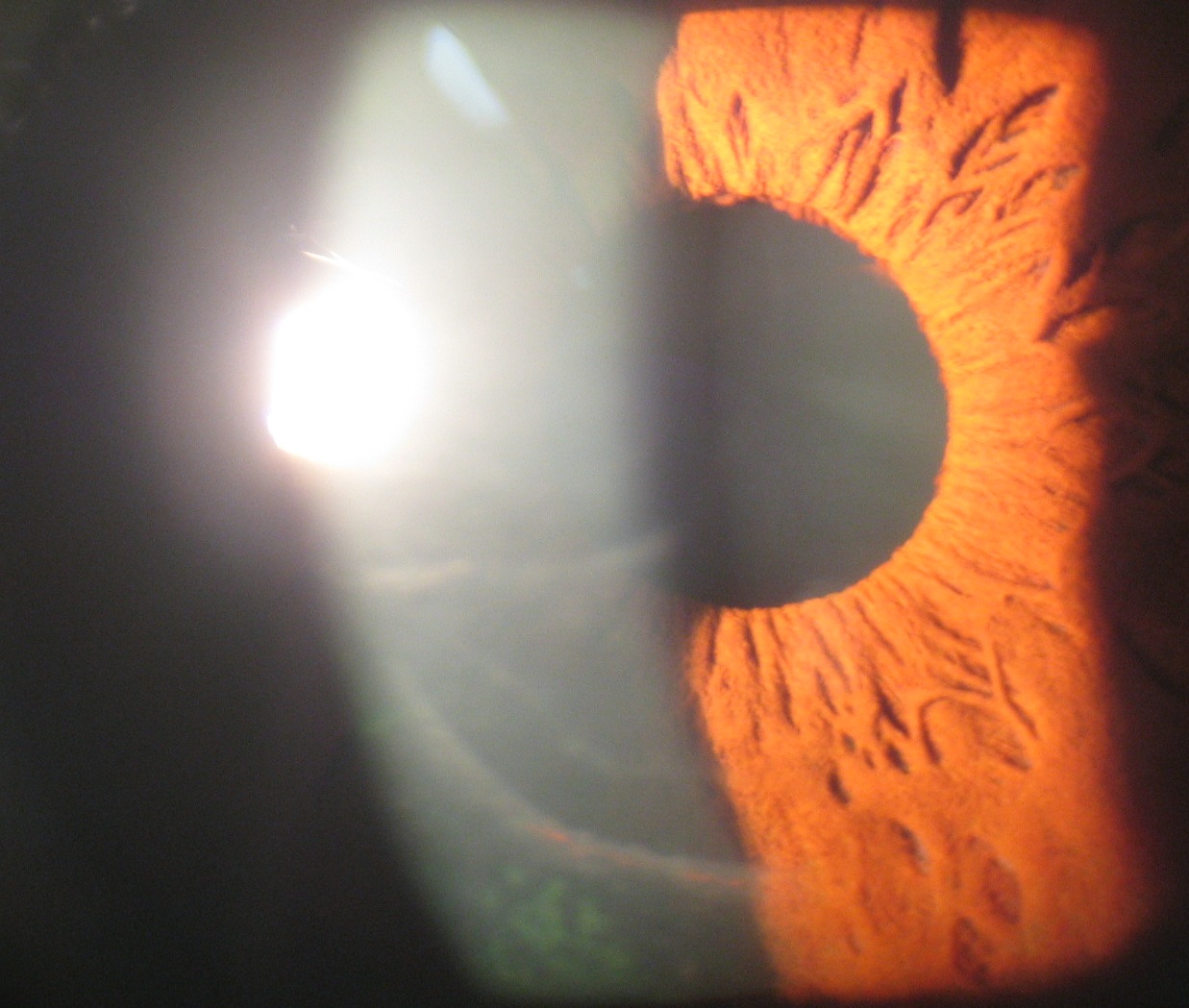
- ICE syndrome
- Inflammatory glaucoma
↑ Outflow
- Wound leak
- Overfiltering bleb
- Ruptured globe
- Cyclodialysis cleft
↓ Production
- Uveitis
- Choroidal / retinal detachment
- Anti-glaucomatous drops
- Ocular ischaemia
- Phthisis bulbi
- (Dehydrated, uraemia, DM, myotonic dystrophy)
“IRATE”
I nflammatory
- Chronic Uveiti
- VKH
- Sympathetic ophthalmia
R etinal Ischaemia
- Proliferative DR
- CRVO
- Ocular ischaemic syndrome
- Radiation
- Chronic retinal detachment
A nterior Segment Ischaemia
- Scleral buckle
- Strabismus surgery
T umours
- Melanoma
- Retinoblastoma
E ndophthalmitis
Undetected High Tension Glaucoma
- POAG (with diurnal variation)
- Prior IOP elevation
- Tonometric error, Thin CCT Cyclodialysis cleft
Non-glaucomatous Optic Nerve Disease
- Congenital- Optic disc pit?, Myopic
- Compression
- AAION
- Toxic - Methanol
Previous
3.1 Glaucoma Examination
All rights reserved. No part of this publication which includes all images and diagrams may be reproduced, distributed, or transmitted in any form or by any means, including photocopying, recording, or other electronic or mechanical methods, without the prior written permission of the authors, except in the case of brief quotations embodied in critical reviews and certain other noncommercial uses permitted by copyright law.
Vitreoretinal Surgery Online
This open-source textbook provides step-by-step instructions for the full spectrum of vitreoretinal surgical procedures. An international collaboration from over 90 authors worldwide, this text is rich in high quality videos and illustrations.