6 Strabismus
6.6 Intermittent Exotropia
- Exophoria (XP) that breaks down to exotropia (XT) when it’s no longer controlled by convergence
- Onset < 5 years (usually ~ 2yrs)
- Parents notice eye is “turned out” under certain conditions (when the child is daydreaming, tired- end of the day, sick)
- Patient closes the affected eye in bright light
- The natural history is debatable. The traditional teaching that intermittent XT progresses towards a constant XT has not been replicated in a retrospective review.[iii]
Romanchuk et. al. Natural History of surgically untreated intermittent exotropia. JAAPOS 2006; 10:225-31.
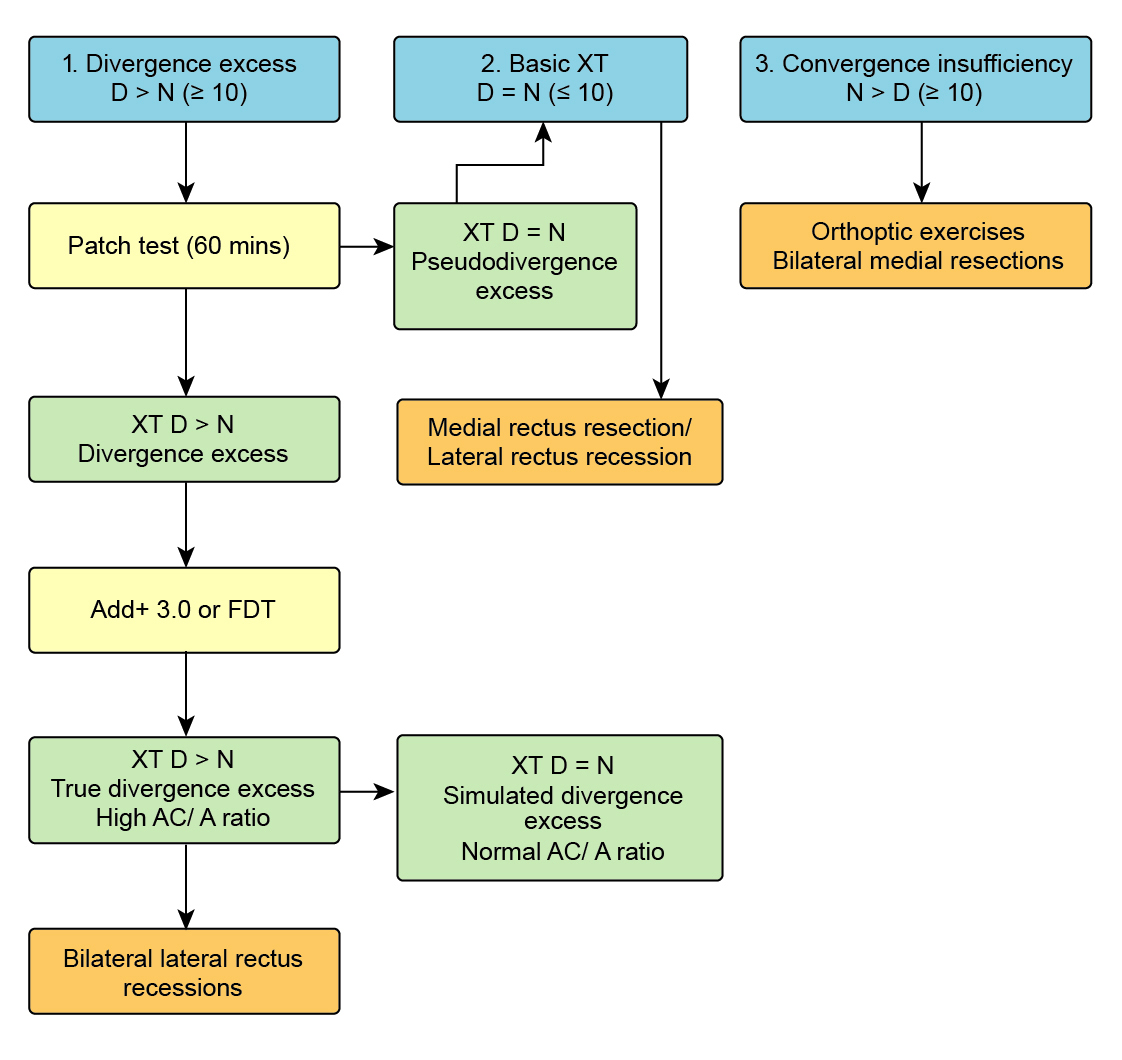
1. Divergence Excess (XT Distance (D) > Near (N) by >10-15Δ, High AC / A)
True
XT still D>N after 1-hour monocular patch or with +3D lens
Pseudo / Simulated
XT D=N after:
1 hour monocular patch (“fusional”)
+ 3D lens (“accommodative”)
Exo deviations for near are controlled by fusional convergence. This control can be abolished by dissociating the eyes with monocular occlusion or removing accommodative drive with a +3D lens. In pseudo-divergence excess, this causes the XT for near to increase to the same degree as that for distance (i.e. it breaks down to a basic XT). The significance of this is debated.
2. Basic (D=N)
3. Convergence Insufficiency (D<N, low AC / A)
- Very rare in young children
- Worse outcomes
- Amblyopia is uncommon
- Abnormal head position?
- Hirschberg (pupil margin=30Δ, limbus=90Δ) - ± Exotropia (at time of examination)
- (Lids normal)
- (Pupils normal)
± Comitant XT
- Without glasses: CTD, CTN
- ± With glasses: CTD, CTN
A. Assess Type
Divergence Excess
XT Distance (D) > Near (N)
Basic
D = N
Convergence Insufficiency
D < N
If divergence excess, test for divergence excess or pseudo-divergence excess by remeasuring after 1 hour of monocular occlusion. If divergence excess is confirmed, test with +3D lenses to differentiate between true and simulated divergence excess, see above)
B. Assess Control
Excellent
Only evident with cover test and controls rapidly
Good
Controls after blink
Fair
Controls after 5 - 10 seconds
Poor
Does not regain control / breaks spontaneously
C. Far Distance
The XT is often worst when asking the patient to look in the far distance (e.g. out a window). However, this may be difficult to examine in young children
- Full ductions
- Usually excellent because straight most of the time
- Exclude sensory XT
Summary
- Intermittent exotropia… divergence excess / basic / convergence insufficiency…
- Excellent / good / fair / poor control
1. Age
- Risk of amblyopia with early surgery
2. Type / Size
- Cosmesis
3. Control (Estimates Binocularity)
- There are scoring systems for this (e.g. Newcastle, Mayo Clinic)
- The size of the tropia does not predict control
- Percentage of day in XT, progressing?
- Vision (amblyopia rare): Binocular VA chart, Worth 4 dot, Synoptophore
- Speed of recovery of tropia (see above)
- Stereopsis for (distance) and near (eyes need to be straight for this)
These methods are rarely definitive, but can be used to delay surgery until the child is older. There is little consensus between clinicians / orthoptists as to best practice
1. Spectacles to Correct Refractive Error
- Myopia, astigmatism, high hypermetropia (consider if >+4D)
Previous
6.5 Accommodative Esotropia
Next
6.7 Duane Syndrome
All rights reserved. No part of this publication which includes all images and diagrams may be reproduced, distributed, or transmitted in any form or by any means, including photocopying, recording, or other electronic or mechanical methods, without the prior written permission of the authors, except in the case of brief quotations embodied in critical reviews and certain other noncommercial uses permitted by copyright law.
Vitreoretinal Surgery Online
This open-source textbook provides step-by-step instructions for the full spectrum of vitreoretinal surgical procedures. An international collaboration from over 90 authors worldwide, this text is rich in high quality videos and illustrations.